
It is important to take precautions to prevent infections, such as getting vaccinated and practicing good hygiene. These infections can damage the auditory nerve and hair cells in the inner ear, leading to ANSD. Infections and Immune System DisordersĪNSD can also result from infections such as meningitis, encephalitis, cytomegalovirus, and other immune system disorders.

It is important for parents to monitor their child’s hearing development and seek medical attention if they notice any signs of hearing loss. Other neonatal factors, such as low birth weight, infections, lack of oxygen to the brain, and use of certain medications, can also contribute to the development of ANSD.

This is because the auditory nerve and hair cells in the inner ear are not fully developed at birth and can be easily damaged. Infants that are born prematurely are at a higher risk of developing ANSD. It is important to note that not all cases of ANSD are caused by genetic factors, and not all people with a genetic predisposition for ANSD will develop the condition. Genetic testing can help identify if a person is at risk of developing ANSD. Several genes have been identified that can cause ANSD, but more research is needed to fully understand the mechanism. Research has shown that ANSD can be inherited in some cases. The causes of ANSD can vary, and in some cases, the cause is unknown. It can affect people of all ages, but it is more commonly diagnosed in infants and young children. Causes of Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum DisorderĪuditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder (ANSD) is a type of hearing loss that occurs when there is damage to the auditory nerve or the hair cells in the inner ear. With the right treatment, many individuals with ANSD are able to improve their hearing and lead fulfilling lives. These may include hearing aids, cochlear implants, and auditory training programs. While ANSD can be a challenging condition to manage, there are a range of treatment options available. For example, research has shown that ANSD may be more common in individuals of African descent. Research has shown that ANSD is more prevalent in certain populations, such as individuals with diabetes or those who have undergone chemotherapy.ĪNSD can affect individuals of any race or ethnicity, but some studies have suggested that certain populations may be more susceptible to the condition. In adults, ANSD is less common than in children and may result from exposure to excessive noise, infections, autoimmune disorders, or genetic conditions. According to research, ANSD accounts for up to 17 percent of hearing loss diagnoses in infants. For example, ANSD is more prevalent in premature infants and those with a family history of hearing loss. While anyone can be affected by ANSD, it is more common in certain populations. The condition can affect individuals of all ages, from infants to adults. This results in a range of hearing difficulties, including difficulty understanding speech, problems with sound localization, and difficulty hearing in noisy environments.ĪNSD is sometimes called Auditory Dys-Synchrony or Auditory Neuropathy/Dys-Synchrony Disorder. In individuals with ANSD, sound passes through the outer ear and middle ear as it should, but the transmission to the inner ear and the brain is defective. What is Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder (ANSD)? Definition and OverviewĪuditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder (ANSD) is a hearing condition that affects the transmission of sound from the outer ear and middle ear to the inner ear and the brain. In this article, we will explore what ANSD is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management.
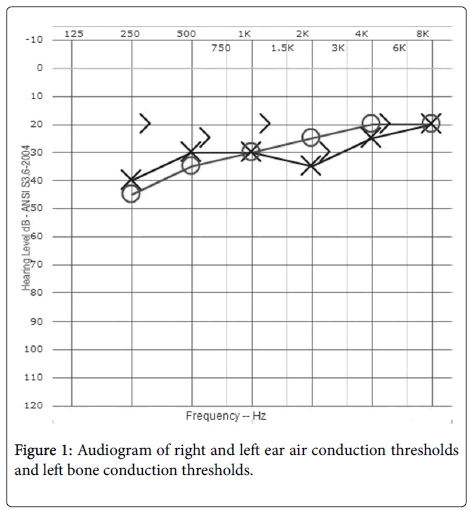
ANSD affects how sound is transmitted from the inner ear to the brain. Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder (ANSD) is a type of hearing impairment that affects both children and adults.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
